Overview
Cardiac arrest-Heart Diseases happens when the heart suddenly stops beating, making it a serious and potentially fatal condition. When this occurs, blood flow to the brain and other vital organs comes to an abrupt halt, causing the person to lose consciousness almost immediately. If help isn’t given right away, it can quickly lead to death. Unlike a heart attack, which is usually due to a blocked artery, cardiac arrest is typically the result of a problem with the heart’s electrical signals. Immediate action, such as CPR and the use of a defibrillator, is crucial to restart the heart and improve the chances of survival.
1. What is Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. This abrupt stop prevents blood from being pumped to the brain and other vital organs. Without this circulation, a person becomes unconscious, stops breathing, and can die within a short time if no help is provided.
The underlying cause of cardiac arrest is usually an electrical disturbance in the heart. This disturbance interrupts the normal rhythm, known as arrhythmia. When the heart’s rhythm becomes chaotic or stops altogether, the heart can no longer pump blood effectively.
2. Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
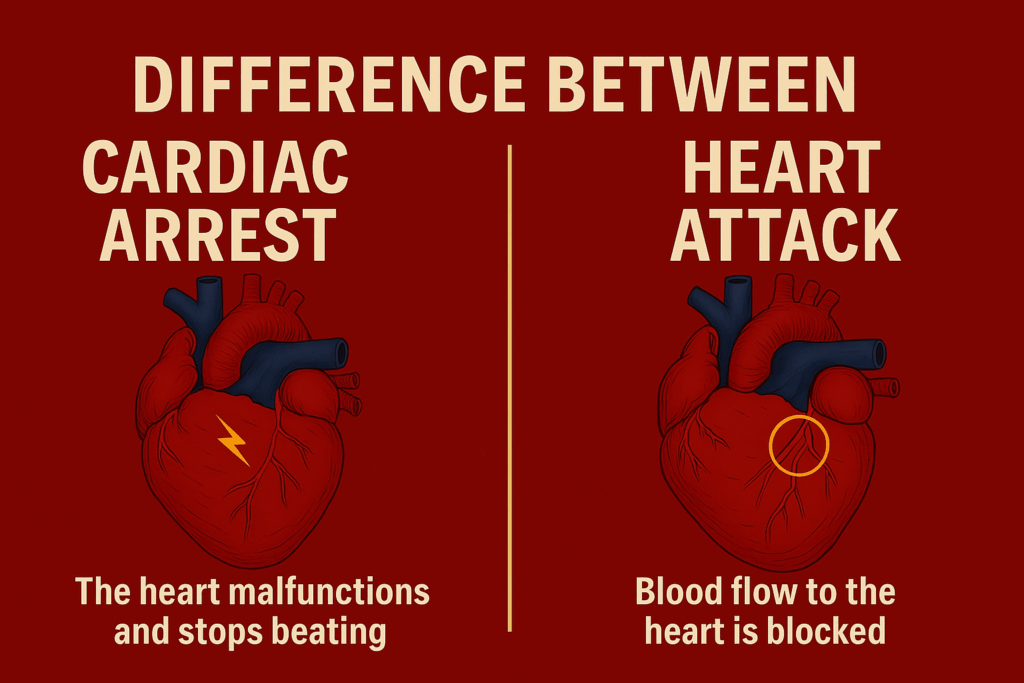
Though often used interchangeably, cardiac arrest and heart attack are not the same:
- A heart attack is caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The heart may continue to beat during a heart attack.
- A cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is an electrical problem where the heart stops functioning altogether.
Interestingly, a heart attack can sometimes trigger cardiac arrest, especially if the heart muscle is severely damaged.
3. Common Causes of Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest can occur in people with or without prior symptoms. However, several heart-related conditions and risk factors can increase the chances of experiencing one:
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart failure
- Enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy)
- Inherited heart rhythm disorders
- Severe arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation
- Substance abuse or overdose
- Severe trauma or loss of blood
Risk is also higher in older adults, smokers, people with high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, or a family history of heart conditions.
4. Warning Signs
In some cases, cardiac arrest may happen without warning. However, a person might experience certain signs beforehand:
- Sudden collapse
- Loss of consciousness
- No pulse or breathing
- Chest discomfort
- Dizziness or palpitations
These signs often come with no time to react, which is why immediate emergency response is vital.
5. Emergency Response and Treatment
When cardiac arrest occurs, immediate action is the only way to save a life:
- Call emergency services right away.
- Begin CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) immediately to maintain blood flow.
- Use an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available, to try and restart the heart.
Every minute without CPR or defibrillation reduces the chance of survival by about 10%. This is why public places now often have AEDs installed and why CPR training is so important.
6. Prevention and Lifestyle
While some cardiac arrests happen without warning, many are linked to long-term heart disease. Therefore, maintaining a healthy heart is the best defense:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet (low in salt, sugar, and saturated fats)
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
- Manage stress and sleep well
- Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
Regular check-ups with a doctor can help catch potential heart issues early, especially if you have risk factors or a family history of heart disease.
Conclusion
Cardiac arrest is one of the most serious medical emergencies, but with the right knowledge and quick action, lives can be saved. Understanding the condition, recognizing the risks, and promoting heart health through lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Whether it’s learning CPR or making healthier choices, everyone has a role to play in fighting heart disease and preventing cardiac arrest.
| Read more: Intermittent Fasting |
| The healthy-life-expert.com crew collected the information via a field visit to provide accurate and genuine information. |