Introduction
The average person’s scalp contains about 100,000 hair follicles. So losing 50 to 100 sheds of hair is absolutely normal and sometimes women lose more hair than men, but if you notice excessive hair shedding, thinning, or random ball patches, you need to see a dermatologist. According to Ayurveda, it is mentioned that “hair fall is an indication of your body that something in your is going wrong unless you fix that bug hair fall won’t be controlled”.
A. Types of Hair Fall
- Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is a very common hair fall in both male and female. It is a genetically predetermined disorder due to an excessive response to androgens. It has no cure.
- Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is the excessive shedding of resting or telogen hair after some metabolic stress, hormonal changes, or medication. Telogen hair is also known as club hair due to the shape of the root. In a normal healthy person’s scalp, about 85% is anagen hair and 15% is telogen hair.
- Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium is a form nonscarring alopecia commonly associated with chemotherapy. The sudden hair loss is caused due to abnormal cessation of the anagen phase due to radiations or infections. This type of hair loss is commonly seen in cancer patients.
- Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is a very common condition of hair loss where some patchy hair loss happens it. Some coined-shaped hair loss happens in it in which no itching and burning happens.
- Tinea Capitis
Tinea Capitis is a fungal infection of scalp hair. It is caused primarily due to the dermatophyte species Microsporum and Trichophyton. The fungi penetrate the hair follicles and invade the hair shaft.
- Cicatricial Alopecia
Cicatricial Alopecia is an inflammatory condition that destroys hair follicles, causing scarring and permanent hair loss. The cause of Cicatricial Alopecia is Lichen planopilaris which is a clinical variant of Lichen planus.
- Hair Shaft Abnormalities
Hair Shaft Abnormalities is a diverse group of abnormalities of the hair shaft. It can occur as an isolated phenomenon or can be associated with an underlying genetic problem. It is characterized by change in colour, density, length and Structure.
- Hypotrichosis
Hypotrichosis a rare form of hereditary hair loss. It is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sparse or absent hair at birth. Hypotrichosis is the medical term for congenital hair follicle deficiency.
B. Causes of different hair fall
| Diseases | Causes |
| a. Androgenetic alopecia | Excessive response to androgens |
| b. Telogen effluvium | Severe protein, fatty acid and Zinc deficit |
| c. Anagen effluvium | Abnormal cessation of the anagen phase from radiations, medication or infections. |
| d. Alopecia areata | Hereditary, Autoimmune disorder |
| e. Tinea Capitis | Dermatophyte species Microsporum and Trichophyton |
| f. Cicatricial Alopecia | Lichen planopilaris |
| g. Hair Shaft Abnormalities | Genetic disorder and Environmental factor |
| h. Hypotrichosis | Mutation in LIPH, LPAR6 or DSG4 gene |
B. Causes of Hair fall
There can be multiple reasons for your hair loss. It can be your food, environment, genetics, and so on.
✓ Anemia
✓ Burns
✓ Autoimmune condition
✓ Excessive shampooing and blow-drying
Deep Study on Alopecia Areata
1. What is Alopecia areata?
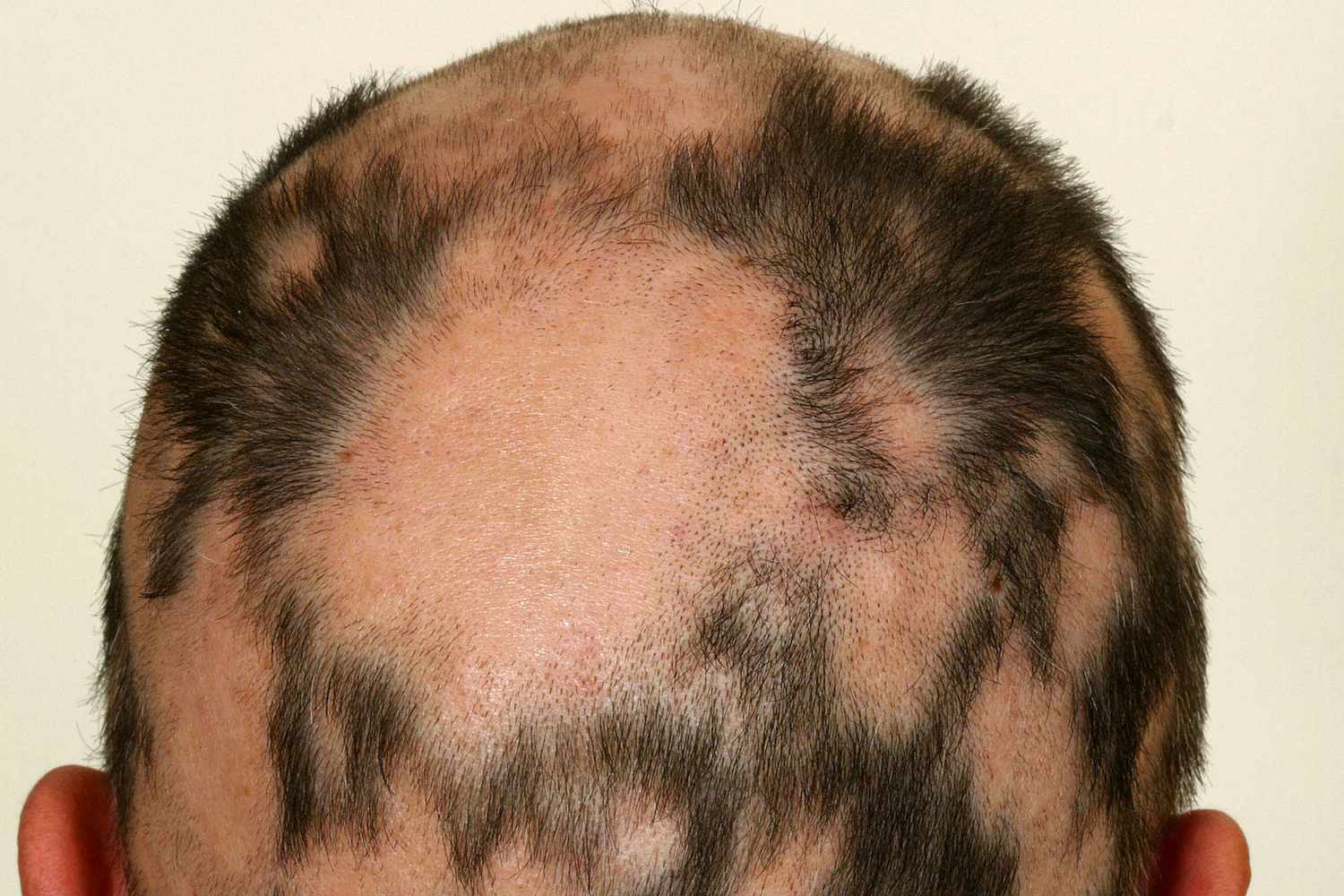
Alopecia areata is a very common condition of hair loss where some patchy hair loss happens it. Some coined-shaped hair loss happens in it in which no itching and burning happens. Generally, it happens mostly in the scalp area and it is seen that it can happen on any hairy area. So we can see some region on the beard region also sometimes on the mustache and sometimes your eyebrow can be affected.
2. Causes of Alopecia areata:
✓ Autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune condition means your immunity goes against its own cells Hair follicle which is the hair-making cell. Now the question may arise “Why this Autoantibody made”. See, so much science is behind it, and many questions are unanswered Why it happen? How it happens? How does it start? No one knows this.
✓ Association with other autoimmune disorders
This disease can happen with other autoimmune conditions like Thyroid or collagen vascular diseases it can be associated with any condition of stress, anxiety, or depression.
3. Diagnosis of Alopecia areata:
✓ Skin biopsy
✓ Identifying associated autoimmune disorders
4. Treatment of Alopecia areata:
✓ Topical medication
✓ Oral medication
5. Some myths about Alopecia areata:
✓ Alopecia areata is contagious. It is not.
✓ There is no treatment.
✓ Hair will never grow back.
✓ Alopecia areata is genetic.
6. How to stop alopecia areata from spreading?
✓ Avoid unnecessary hair or scalp trauma.
✓ Reducing stress.
✓ Invest in corticosteroid treatment.
✓Analyzing the diet.
7. Why is my hair falling out?
There can be a list of reasons for your hair fall. Here are some reasons:
✓ Heredity
✓ Vitamins and mineral deficiency
✓ Childbirth and illness
✓ Infection and surgery
But the good news is none of those causes of hair fall are permanent. However excessive shedding can also be an indication of potential medical conditions like auto immune diseases, or hormonal imbalance so the best thing you can do is go to your doctor to solve all these things out specially since excessive shedding is happening for more than 4 months.
8. How to stop hair fall immediately?
The following things should do:
✓ Blood test
✓ Peptide serum
✓ Taking a balanced diet
✓ Avoid treatment
✓ Keeping the scalp clean
| Read more: White Flour: Is it harmful? |
| The healthy-life-expert.com crew collected the information via a field visit to provide accurate and genuine information. |